
This account is grounded on experimental practices of stem cell research, with emphasis on new techniques for generating biological organization in vitro.

This paper aims to fill the gap, proposing the lineage view of stem cells as an ontological framework for conceptualizing organismal development. However, recent accounts of these concepts do not engage developmental biology. The process of development is thus prima facie central for ideas about biological individuality and organismality. Biological development is a process, undergone by living things, which begins with a single cell and (in an important class of cases) ends with formation of a multicellular organism. Ontologies of living things are increasingly grounded on the concepts and practices of current life science. Visit the Stem Cell Interest Group Web site to learn more.Received 2 September 2016 Accepted 20 February 2017 Abstract In addition to the research programs within the IRP, the NIH Stem Cell Interest Group was established to enhance communication and collaboration among scientist interested in stem cells.
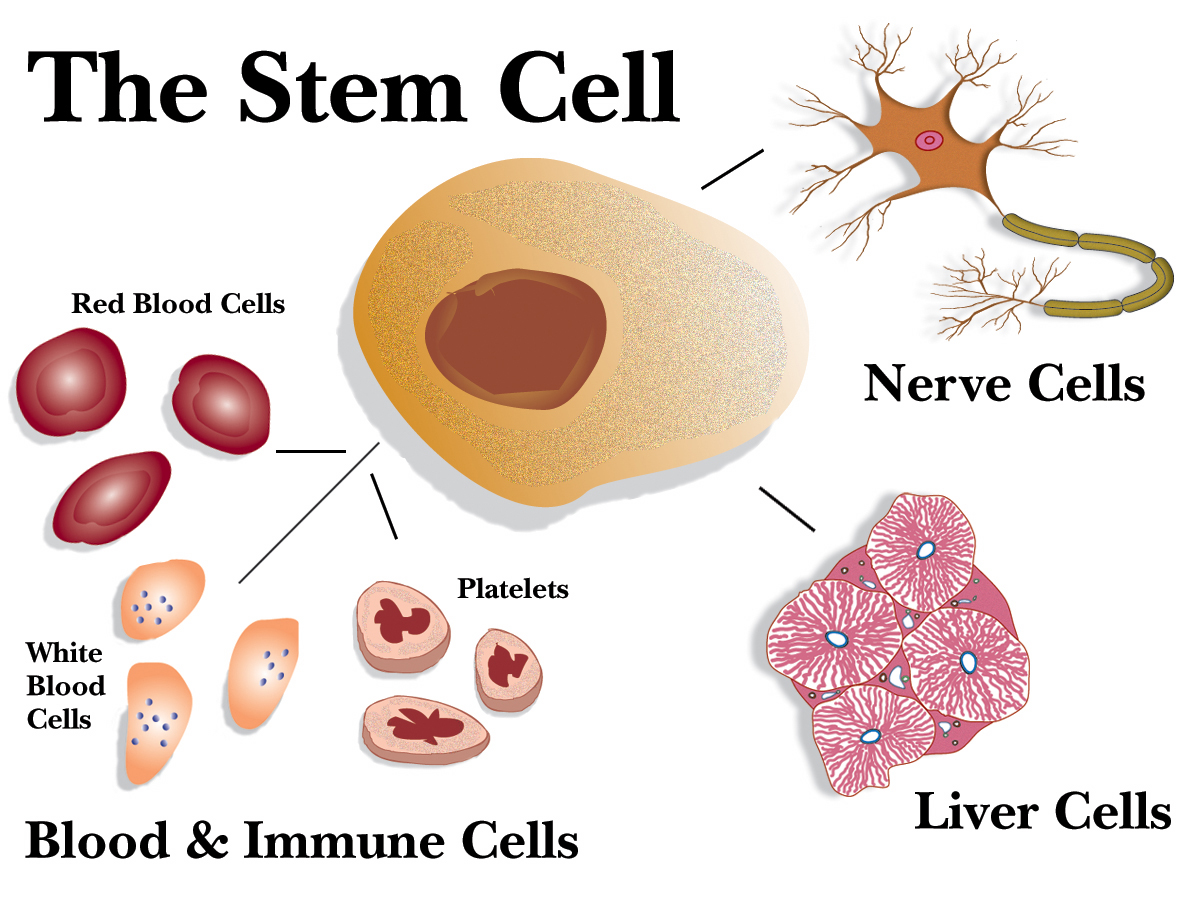
Manipulating stem cells to become bone and cartilageĪdditionally, the NIH Regenerative Medicine Program (RMP) is a resource that provides infrastructure to accelerate the clinical translation of stem cell-based therapies-at any one time, around 100 clinical trials investigating the use of stem cells as therapies are ongoing at the NIH Clinical Center.Reprogramming tumor-specific immune cells from stem cells for cancer immunotherapy.Investigating the use of stem cells to study and treat Gaucher disease and parkinsonism.Stimulating an anti-brain tumor immune response via manipulated stem cells.Creating insulin-producing pancreatic beta cells for clinical trials in diabetes.Creating stem cell-derived neurons for the study of motor neuron disease.Treating liver disease with stem cells that have been manipulated to become specialized liver cells.Many of the Institutes and Centers of the Intramural Research Program (IRP) have a dedicated stem cell research program, including the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI), National Institute of Dental Craniofacial Research (NIDCR), National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), and the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS).Īreas of active research on stem cell biology within these programs include: There are three primary types of stem cells: embryonic stem cells are characterized as pluripotent in nature-capable of developing into the two hundred or so specialized cells of the adult organism adult stem cells exist within certain tissues of the body (for example, blood and bone marrow) and carry out repair and regenerative functions and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are adult stem cells that have been genetically reprogrammed to behave like embryonic stem cells.ĭue to their ability to repair, regenerate, and develop into certain specialized cell types, stem cells offer great promise as therapy for a number of diseases. Stem cells are a specific type of cell capable of evolving into many different types of specialized cells within the body. View Principal Investigators in Stem Cell Biology


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
