
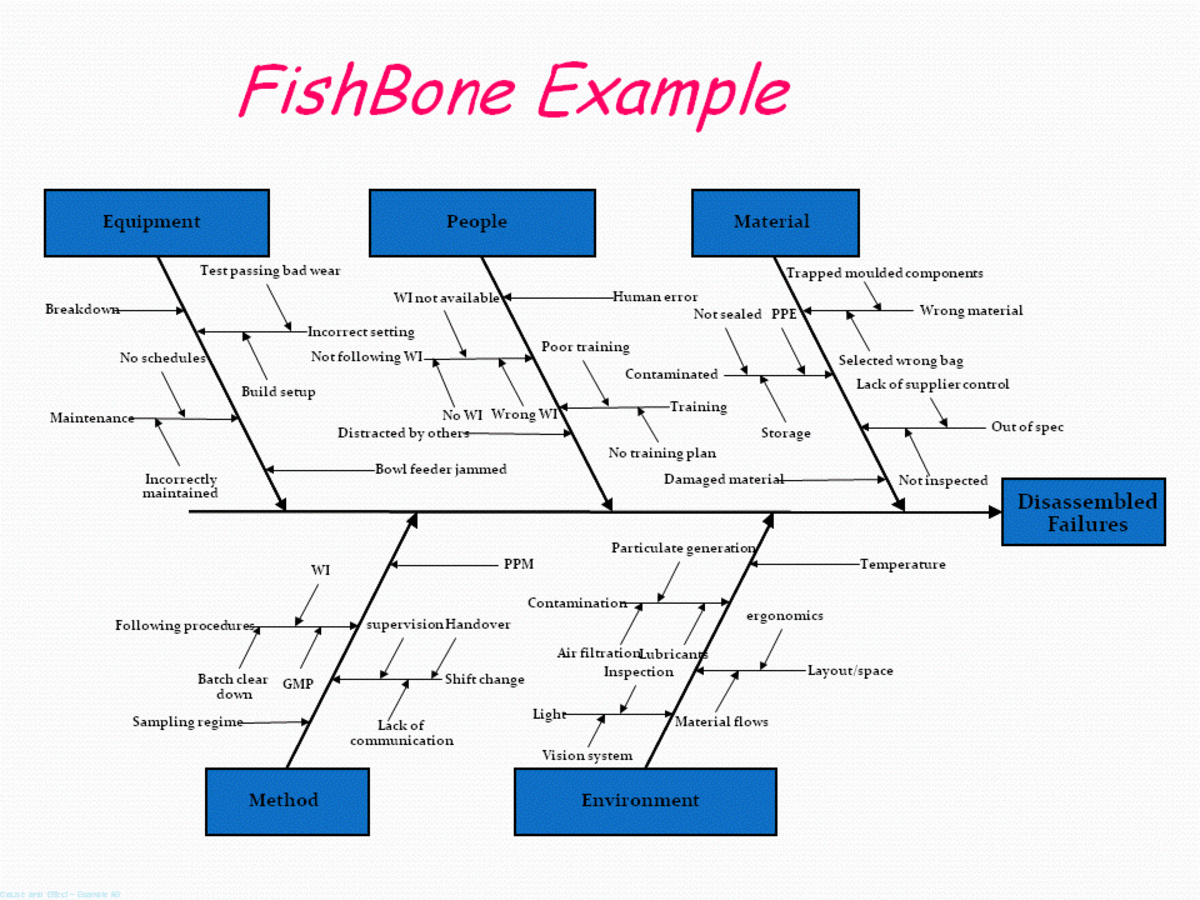
Through constructing the graphic, teams come to articulate an issue, which makes finding the cause of the problem easier. You can also apply 6M and 5W1H method in cause and effect analysis for better solutions. The fishbone diagram is a visual representation of the cause and effects of a problem.
#Fishbone ishikawa diagram how to
And it ensures that nobody is wasting energy chasing nonexistent problems.Ĭheck out the following example to see how to apply 8P method in cause and effect analysis to It helps to analyze every involved party. Help maintain team focus - The fishbone framework can keep your team focused as you discuss what should be done to solve the problem or achieve a common goal. Stimulate problem solving - Seeing the reasons in visual graph and exploring the root cause may stimulate your team to find out possible solutions to the problems.ĥ. Facilitate brainstorming - Edraw fishbone diagram is a great way to boost and structure brainstorming about the reasons for a certain result because it captures all the causes.Ĥ. This makes it a useful tool for presenting the problem and solutions to stakeholders.ģ.
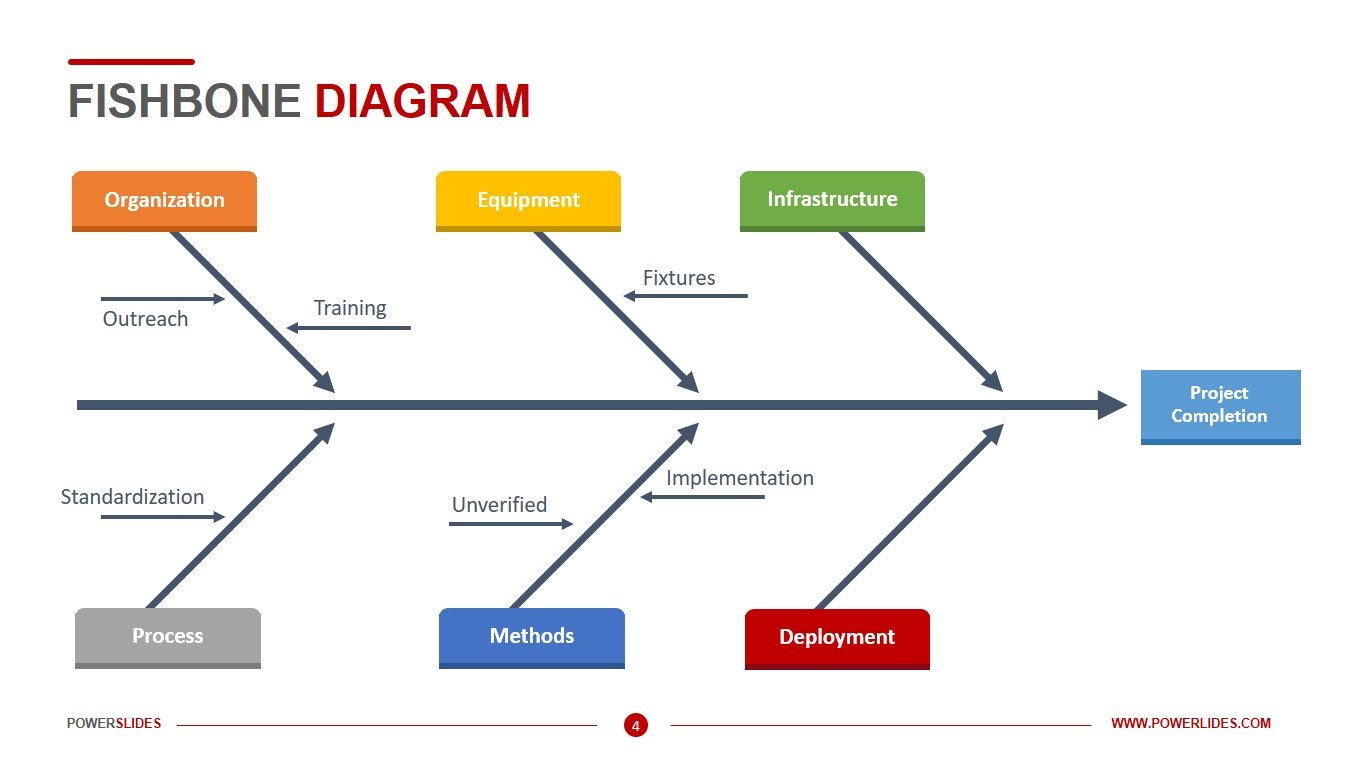
The fishbone diagram illustrates each and every possible reason in a single diagram, which is beneficial for in-depth analysis. Show all causes simultaneously - Any cause or causal chain featured on the fishbone diagram could lead to the problem. Categorized logically, the correlation can be understood at a glance.Ģ. Display relationships clearly and logically - The fishbone diagram captures the links and relationships among the potential causes and results displayed in the diagram. Interested in expanding your knowledge on Lean Six Sigma? Take your career to the next level and join ISSSP today! Access the hundreds of videos, webinars, whitepapers, case studies, and other resources available in our library.Fishbone diagrams are very useful because they portray information in a neat and comprehensible way. SuggestionsĬonsider using the Reverse Fishbone during the Pilot Project implementation in the Improve Phase of your Lean Six Sigma project in order to analyze the effects of your improvement solution(s).ĭon’t you wish that all government policymakers would at least sit down and do a simple reverse fishbone analysis before rolling out a new directive? An article published by the Meeting Tool Chest describes the diagram and gives some guidance for its use. In a presentation titled “Using QI Tools: Action Effect Diagrams” from Healthy London by Tom Woodcock we learn how the Action Effect Diagram can be used in the healthcare field.Īlso, as we mentioned earlier, yet another name for the Reverse Fishbone Diagram is the Solution Effect Diagram. To go directly to the discussion of the reverse fishbone, start the video at 10:20.Įarlier we mentioned that another name for the reverse fishbone diagram is the Action Effect Diagram. In another video from I-Nexus, Christian Loyer discusses the traditional fishbone and the reverse fishbone diagrams. We’ll start with a video from Dennis Taboada, CEO of DTI Training Consortium introducing the Reverse Fishbone Diagram with a simple example. We brainstorm how the proposed change impacts these areas. Potential impact areas, which could be the usual People, Methods, Materials, Measurement, Machines, and Environment are the bones. The proposed change is at the head of the fish. Impact Analysis Diagram or Change Impact Analysis Diagram.The method was created by Kaoru Ishikawa in the 1960s. Solution Impact Diagram or Solution Effect Diagram Also known as a Cause and Effect diagram, or Ishikawa diagram.Other names for the Reverse Fishbone Diagram include:


We will look at the Reverse Fishbone Diagram which is used to analyze the impacts of a change. We’re very familiar with the Fishbone Diagram (Cause and Effect Diagram), also known as the Ishikawa Diagram, whereby we analyze the potential causes of a given effect.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
