
She Was a World War I HeroĬurie helped save thousands of soldiers by developing mobile radiology units that were delivered to the front lines for army doctors to use. Turns out Team Curie opted to work out of an old shed for much of their Nobel prize-winning research.
WHO HELPED DISCOVER RADIUM AND POLONIUM SERIES
When Marie and her husband sought to conduct a series of experiments that would prove the existence of the elements radium and polonium, they needed plenty of space - a traditional laboratory just didn't make the cut. Marie Curie may have broken barriers in science, but her lab was far from glamorous. When you think of a Nobel Prize-winning physicist, you can only imagine how legit their workspace must be. Here are five fun facts about Marie Curie, a radiant woman who paved the way for women in science : 1. What Are Some Interesting Facts About Marie Curie? Today, Marie Curie's discoveries on the properties of radioactive elements have paved the way for diagnosis and radiation therapy in medicine. In 1911, she became the sole recipient of the Nobel Prize for chemistry for her work on pure radium. Even though Marie became the first woman to receive a Nobel Prize, she didn't stop there. The term radioactivity was coined by Marie herself and garnered the world's attention.įor their groundbreaking work, the pair received the Nobel Prize in physics in 1903. They shared a love for science and research, which led to their ground-breaking discovery of radioactivity - the spontaneous emission of energetic particles or waves via unstable atomic nuclei. Soon after, she met her husband and science partner, Pierre Curie. There she discovered two radioactive elements: radium and polonium. The new element, the radium, became an extraordinary tool for the early exploration of the structure of matter and also for its therapeutical applications.In 1891, her French came in handy as the young scientist headed for Paris to further her education at Sorbonne University, where she studied chemistry, maths and physics. In 1903, Pierre et Marie Curie were rewarded by a Nobel Prize shared with Henri Becquerel (in 1911 Marie Curie was again rewarded by a second Nobel Prize). Marie Curie was able to narrow down the accuracy on radium atomic mass to 1 nucleon. The atomic mass is today defined as the total number of protons and neutrons forming up a nucleus. Marie Curie was able to show that radium filled in one of these pieces in the jigsaw, and demonstrated that it had an atomic mass of 226. In 1902, Mendeleyev’s periodic table still had gaps. Radium salts also possess a remarkable quality: they glow in the dark, are warm to the touch and seem to give off an inexhaustible supply of heat. Pierre Curie immediately understood the importance of these observations and together with his wife discovered two previously unknown elements in 1898: polonium and radium, present in trace amounts in pitchblende.įrom several tonnes of pitchblende residue, Marie Curie was able to isolate pure radium, an element which is a million times more radioactive than uranium. She added that the origin of the phenomenon must be inside the atom, as radioactivity occurs on a submolecular level.
Marie Curie then proposed the hypothesis that the property of emitting these rays was a more general property of matter, which she named ‘radioactivity’. Like pitchblende, chalcolite is a mineral often found in lead mines. Pitchblende is a mineral rich in uranium, that was used in the 19th Century to add colour to Bohemian crystals.

Uranium is a rare element(present in 3 parts per million on the Earth’s crust). Marie Curie carried out these measurements and discovered that thorium also emits these ‘Becquerel rays’, and that uranium minerals such as pitchblende and chalcolite have infinitely more intense emissions that pure uranium.
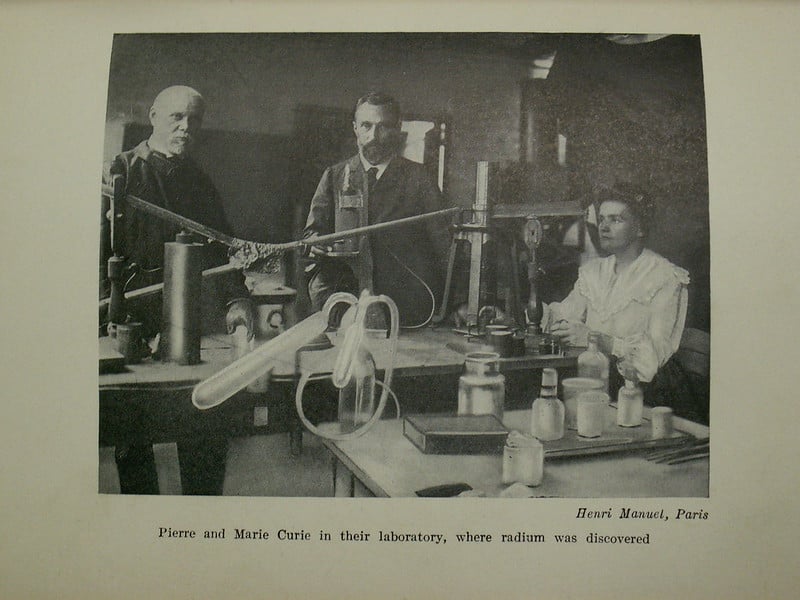

She measured their ability to electrify the air surrounding them with a piezoelectric quartz electrometer invented by Pierre and Jacques Curie, capable of measuring very low values of electric intensity. In November 1897, Marie Curie decided to conduct systematic research on the ‘uranic rays’ found in a number of elements, compounds and minerals. Pierre Curie died in 1906 as the result of a tragic road accident. He abandoned his own research to work with Marie Curie on the then unknown elements responsible for the Becquerel rays.

Pierre Curie was already renowned for his work on piezoelectricity, the symmetry of crystals, and magnetism. Pierre and Marie Curie in 1898, in the ‘discovery shed’ at the Ecole de Physique et Chimie Industrielles then situated at 42 rue Lhomond in Paris.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
